Plants Watering Watcher
Varying brightness LED signals the necessity to water a plant
Very low consumption, 3V powered circuit
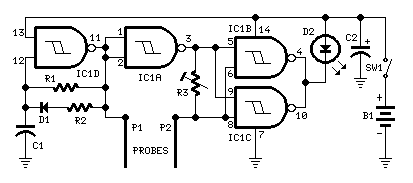
Circuit diagram
Parts:
- R1 470K 1/4W Resistor
- R2 3K3 1/4W Resistor
- R3 100K 1/2W Trimmer Cermet
- C1 1nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
- C2 47µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
- D1 1N4148 75V 150mA Diode
- D2 5mm. Red LED
- IC1 4093 Quad 2 input Schmitt NAND Gate IC
- P1,P2 Probes (See text)
- SW1 SPST Slider Switch
- B1 3V Battery (2 AA 1.5V Cells in series)
Device purpose:
This circuit is intended to signal when a plant is needing water. A LED illuminates at maximum brightness when the ground in the flower-pot is too dry: it dims gradually as the water's content in the pot grows, turning off when the optimum moisture's level is reached. This condition is obtained trimming R3.
Circuit operation:
IC1D forms a square wave oscillator with approx. 10/90 mark-space ratio. It feeds the output probe P1 and its signal, inverted by IC1A is compared with that picked-up by P2 in the NAND gates IC1B & IC1C in parallel, driving the LED. When a low resistance exists between the probes, due to an high water's content in the flower-pot, the LED is off, turning gradually on as the resistance between the probes increases.
Notes:
- A square wave is used to avoid probes' oxidization.
- Probes can be long nails, carbon rods obtained from disassembled exhausted 1.5V batteries, or even a couple of screwdrivers.
- The probes must be driven in the pot's ground a few inches apart.
- Due to 3V supply, the LED needs not a limiting resistor.
- Power consumption: LED off = 50µA; LED full on = 1mA.
- To switch-off the circuit, you can short the probes. In this case SW1 can be omitted.
- Using an high-efficiency LED, brightness variations are better emphasized. In this case a limiting resistor could be necessary.
circuit from http://www.redcircuits.com/