Temperature sensor schematics
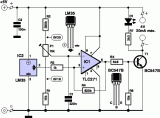 It sounds rather mysterious: a switch that is controlled by its ambient temperature. All without the touch of a human hand, except for when you’re building this sort of electronic thermostat. There are a lot of handy uses for a thermally controlled switch. If the temperature inside your PC gets too high sometimes, the circuit can switch on an extra fan. You can also use to switch on an electric heater automatically if the room temperature is too low. There are innumerable potential applications for the thermostat described here....
[read more]
It sounds rather mysterious: a switch that is controlled by its ambient temperature. All without the touch of a human hand, except for when you’re building this sort of electronic thermostat. There are a lot of handy uses for a thermally controlled switch. If the temperature inside your PC gets too high sometimes, the circuit can switch on an extra fan. You can also use to switch on an electric heater automatically if the room temperature is too low. There are innumerable potential applications for the thermostat described here....
[read more]
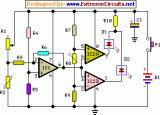 This sensitive circuit is basically a comparator, detecting very slight temperature changes in respect to the ambient temperature. It was primarily intended to detect draughts around doors and windows that cause energy leaks but can be used in many other ways, when a sensitive temperature change detector is needed. Two LEDs are used to signal if the temperature change is pointing above (Red LED) or below (Green LED) the ambient temperature....
[read more]
This sensitive circuit is basically a comparator, detecting very slight temperature changes in respect to the ambient temperature. It was primarily intended to detect draughts around doors and windows that cause energy leaks but can be used in many other ways, when a sensitive temperature change detector is needed. Two LEDs are used to signal if the temperature change is pointing above (Red LED) or below (Green LED) the ambient temperature....
[read more]
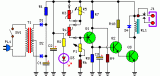 This circuit is intended to control a heating system or central heating plan, keeping constant indoor temperature in spite of wide range changes in the outdoor one. Two sensors are needed: one placed outdoors, in order to sense the external temperature; the other placed on the water-pipe returning from heating system circuit, short before its input to the boiler....
[read more]
This circuit is intended to control a heating system or central heating plan, keeping constant indoor temperature in spite of wide range changes in the outdoor one. Two sensors are needed: one placed outdoors, in order to sense the external temperature; the other placed on the water-pipe returning from heating system circuit, short before its input to the boiler....
[read more]
 It beeps if the fridge door is left open for too long or hasn't closed properly, to stop food from spoiling. There are lots of other uses as well. A refrigerator or freezer door that is left open or ajar may cause the food contents to spoil. In some cases, the internal temperature of the fridge or freezer will be maintained if the refrigeration system can cope with the open door....
[read more]
It beeps if the fridge door is left open for too long or hasn't closed properly, to stop food from spoiling. There are lots of other uses as well. A refrigerator or freezer door that is left open or ajar may cause the food contents to spoil. In some cases, the internal temperature of the fridge or freezer will be maintained if the refrigeration system can cope with the open door....
[read more]
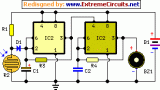 The circuit, enclosed in a small box, should be placed in the fridge near the lamp (if any) or close to the opening. With the door closed, the interior of the fridge is in dark, the photo resistor R2 presents a high resistance (>200K) thus clamping IC1 by holding C1 fully charged across R1 and D1. When a beam of light enters from the opening, or the fridge lamp lights, the photo resistor lowers its resistance (<2K) stopping C1 charging current....
[read more]
The circuit, enclosed in a small box, should be placed in the fridge near the lamp (if any) or close to the opening. With the door closed, the interior of the fridge is in dark, the photo resistor R2 presents a high resistance (>200K) thus clamping IC1 by holding C1 fully charged across R1 and D1. When a beam of light enters from the opening, or the fridge lamp lights, the photo resistor lowers its resistance (<2K) stopping C1 charging current....
[read more]
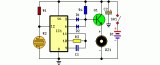 This circuit, enclosed into a small box, is placed in the fridge near the lamp (if any) or the opening. With the door closed the interior of the fridge is in the dark, the photo resistor R2 presents a high resistance (up to 200K) thus clamping IC1 by holding pin 12 high. When a beam of light enters from the opening, or the fridge lamp illuminates, the photo resistor lowers its resistance (less 2K), pin 12 goes low, IC1 starts counting and, after a preset delay (20 seconds in this case) the piezo sounder beeps for 20 sec. then stops for the same lapse of time and the cycle repeats until the fridge door closes. D2 connected to pin 6 of IC1 allows the piezo sounder beeping 3 times per second....
[read more]
This circuit, enclosed into a small box, is placed in the fridge near the lamp (if any) or the opening. With the door closed the interior of the fridge is in the dark, the photo resistor R2 presents a high resistance (up to 200K) thus clamping IC1 by holding pin 12 high. When a beam of light enters from the opening, or the fridge lamp illuminates, the photo resistor lowers its resistance (less 2K), pin 12 goes low, IC1 starts counting and, after a preset delay (20 seconds in this case) the piezo sounder beeps for 20 sec. then stops for the same lapse of time and the cycle repeats until the fridge door closes. D2 connected to pin 6 of IC1 allows the piezo sounder beeping 3 times per second....
[read more]
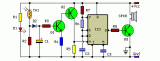 In this fire alarm circuit, a Thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases, its resistance decreases, and vice versa. At normal temperature, the resistance of the Thermistor (TH1) is approximately 10 kilo-ohms, which reduces to a few ohms as the temperature increases beyond 100 C. The circuit uses readily available components and can be easily constructed on any general-purpose PCB....
[read more]
In this fire alarm circuit, a Thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases, its resistance decreases, and vice versa. At normal temperature, the resistance of the Thermistor (TH1) is approximately 10 kilo-ohms, which reduces to a few ohms as the temperature increases beyond 100 C. The circuit uses readily available components and can be easily constructed on any general-purpose PCB....
[read more]
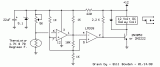 Here is a simple thermostat circuit that can be used to control a relay and supply power to a small space heater through the relay contacts. The relay contacts should be rated above the current requirements for the heater....
[read more]
Here is a simple thermostat circuit that can be used to control a relay and supply power to a small space heater through the relay contacts. The relay contacts should be rated above the current requirements for the heater....
[read more]
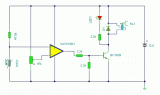 Using a thermistor in the position shown makes a heat activated sensor. A change in temperature will alter the output of the opamp and energize the relay and light the LED. Swapping the position of the thermistor and 47k resistor makes a cold or frost alarm....
[read more]
Using a thermistor in the position shown makes a heat activated sensor. A change in temperature will alter the output of the opamp and energize the relay and light the LED. Swapping the position of the thermistor and 47k resistor makes a cold or frost alarm....
[read more]
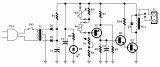 This circuit is intended to control a heating system or central heating plan, keeping constant indoor temperature in spite of wide range changes in the outdoor one....
[read more]
This circuit is intended to control a heating system or central heating plan, keeping constant indoor temperature in spite of wide range changes in the outdoor one....
[read more]
 This circuit, enclosed in a small box, is placed in the fridge near the lamp (if any) or the opening....
[read more]
This circuit, enclosed in a small box, is placed in the fridge near the lamp (if any) or the opening....
[read more]
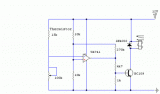 The thermistor used has a resistance of 15k at 25 degrees and 45k at 0 degrees celsius....
[read more]
The thermistor used has a resistance of 15k at 25 degrees and 45k at 0 degrees celsius....
[read more]
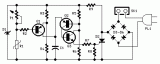 This circuit adopt a rather old design technique as its purpose is to vary the speed of a fan related to temperature with a minimum parts counting and avoiding the use of special-purpose ICs, often difficult to obtain....
[read more]
This circuit adopt a rather old design technique as its purpose is to vary the speed of a fan related to temperature with a minimum parts counting and avoiding the use of special-purpose ICs, often difficult to obtain....
[read more]
 This circuit controls a load (in this case a dc brushless fan) based on a temperature compared with a setpoint. THe transduced is a diode in the forward polarization regime. In fact when forward biased, the forward voltage drop accross a diode has a temperature dependance, in particular has a negative linear(ish) slope. This because of the boltzmann distribuition, causing electrons to pass to the conduction band thermically, lowering the voltage drop accross the diode....
[read more]
This circuit controls a load (in this case a dc brushless fan) based on a temperature compared with a setpoint. THe transduced is a diode in the forward polarization regime. In fact when forward biased, the forward voltage drop accross a diode has a temperature dependance, in particular has a negative linear(ish) slope. This because of the boltzmann distribuition, causing electrons to pass to the conduction band thermically, lowering the voltage drop accross the diode....
[read more]
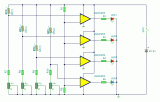 A simple device to indicate various levels of hot water in a tank....
[read more]
A simple device to indicate various levels of hot water in a tank....
[read more]
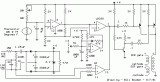 The heater element (not shown) is connected in series with two back to back 16 amp SCRs (not shown) which are controlled with a small pulse transformer. The pulse transformer has 3 identical windings, two of which are used to supply trigger pulses to the SCRs, and the third winding is connected to a PNP transistor pair that alternately supply pulses to the transformer at the beginning of each AC half cycle. The trigger pulses are applied to both SCRs near the beginning of each AC half cycle but only one conducts depending on the AC polarity....
[read more]
The heater element (not shown) is connected in series with two back to back 16 amp SCRs (not shown) which are controlled with a small pulse transformer. The pulse transformer has 3 identical windings, two of which are used to supply trigger pulses to the SCRs, and the third winding is connected to a PNP transistor pair that alternately supply pulses to the transformer at the beginning of each AC half cycle. The trigger pulses are applied to both SCRs near the beginning of each AC half cycle but only one conducts depending on the AC polarity....
[read more]