Welcome!
Please, enjoy our completely free circuit diagrams and electronics projects database!
Random circuits
Here are some of over 800 projects from our free circuit diagrams database. For more, try browsing categories menu on the left.
 This simple logic probe has both LEDs on with no signal at the input but due to the nor gates connected to the probe, indicates correctly when a high or low signal is present. It also works correctly for pulse trains. Normally both LEDs are forward biased and therefore on, powered by the 12V supply. When a logic "high" is present at the probe, IC1a's output goes low sending IC1b's output high. This turns off LED1 but forward-biases (and turns on) LED2. Conversely, a logic "low" at the probe will send IC1b low, turning LED1 on and LED2 off....
[read more]
This simple logic probe has both LEDs on with no signal at the input but due to the nor gates connected to the probe, indicates correctly when a high or low signal is present. It also works correctly for pulse trains. Normally both LEDs are forward biased and therefore on, powered by the 12V supply. When a logic "high" is present at the probe, IC1a's output goes low sending IC1b's output high. This turns off LED1 but forward-biases (and turns on) LED2. Conversely, a logic "low" at the probe will send IC1b low, turning LED1 on and LED2 off....
[read more]
 It beeps if the fridge door is left open for too long or hasn't closed properly, to stop food from spoiling. There are lots of other uses as well. A refrigerator or freezer door that is left open or ajar may cause the food contents to spoil. In some cases, the internal temperature of the fridge or freezer will be maintained if the refrigeration system can cope with the open door....
[read more]
It beeps if the fridge door is left open for too long or hasn't closed properly, to stop food from spoiling. There are lots of other uses as well. A refrigerator or freezer door that is left open or ajar may cause the food contents to spoil. In some cases, the internal temperature of the fridge or freezer will be maintained if the refrigeration system can cope with the open door....
[read more]
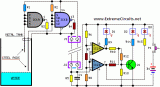 When the water-level is below the steel rods, no contact is occurring from the metal can and the rods, which are supported by a small insulated (wooden) board. The small circuit built around IC1 draws no current and therefore no voltage drop is generated across R5. IC2A, IC2B and Q1 are wired as a window comparator and, as there is zero voltage at input pins #2 and #5, D3 will illuminate. When the water comes in contact with the first rod, pin #13 of IC1 will go high, as its input pins #9 to #12 were shorted to negative by means of the water contact....
[read more]
When the water-level is below the steel rods, no contact is occurring from the metal can and the rods, which are supported by a small insulated (wooden) board. The small circuit built around IC1 draws no current and therefore no voltage drop is generated across R5. IC2A, IC2B and Q1 are wired as a window comparator and, as there is zero voltage at input pins #2 and #5, D3 will illuminate. When the water comes in contact with the first rod, pin #13 of IC1 will go high, as its input pins #9 to #12 were shorted to negative by means of the water contact....
[read more]
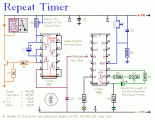 This circuit has an adjustable output timer that will re-trigger at regular intervals. The output period can be anything from a fraction of a second to half-an-hour or more - and it can be made to recur at regular intervals of anything from seconds to days and beyond....
[read more]
This circuit has an adjustable output timer that will re-trigger at regular intervals. The output period can be anything from a fraction of a second to half-an-hour or more - and it can be made to recur at regular intervals of anything from seconds to days and beyond....
[read more]
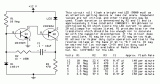 Two Transistor LED Flasher...
[read more]
Two Transistor LED Flasher...
[read more]
 This is a Universal version of the Four-Digit Alarm Control Keypad. I have modified the design to free up the relay contacts. This allows the circuit to operate as a general-purpose switch. I've used a SPCO/SPDT relay - but you can use a multi-pole relay if you wish....
[read more]
This is a Universal version of the Four-Digit Alarm Control Keypad. I have modified the design to free up the relay contacts. This allows the circuit to operate as a general-purpose switch. I've used a SPCO/SPDT relay - but you can use a multi-pole relay if you wish....
[read more]